
■ Features
Your complete guide to music royalties – from understanding the types of royalties to maximizing your earnings and protecting your creative work.
Royalties. It’s a word that you may have heard often, likely in reference to a dispute between artists, songwriters, and labels. As a creator, you should have an understanding of music royalties before even entering music production spaces with collaborators. This is the only way to avoid problems such as these further down the line.
If you're someone who is interested in how to make music, and vaguely interested in how to make money from said music at some point, you may have an idea of what the word means, but do you understand it as well as you should? What are royalties in music, really?
As a major source of income for songwriters, composers, performers, and music publishers, music royalties are a crucial component of the music business. These royalties are sums of money given to musicians in exchange for the usage of their musical compositions, whether it be through online music services, radio airplay, TV advertising, or live performances.
Due to the growth of digital streaming services, the music industry has undergone tremendous upheaval in recent years, creating new opportunities and problems for music royalties. As we all know by this point, there are very few income streams left in music, and anyone wishing to make a living in the business must have a thorough understanding of the nuances of music royalties.
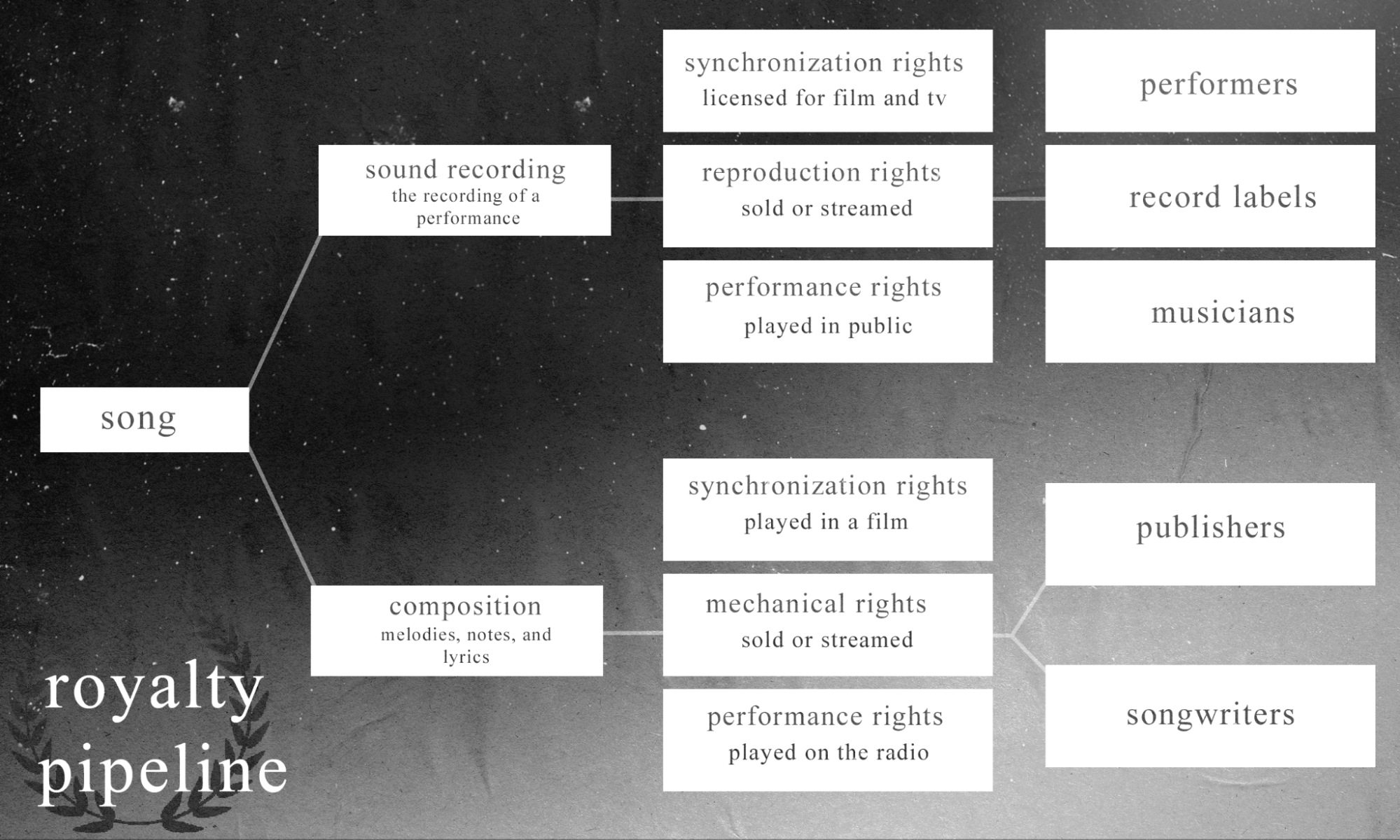
A legal concept known as "sound recording copyright" safeguards the rights of the creators of any type of audio recording, including songs, albums, and other audio recordings. The owner is given the sole authority to reproduce, distribute, and perform the sound recording in public thanks to copyright protection. Sound recording copyright is normally controlled by record companies in the music industry, although it can also be owned by independent musicians or producers.
Songwriting copyright is a legal concept that safeguards the rights of composers and songwriters. It gives them sole ownership of their musical creations, including the freedom to copy, share, perform, and broadcast their tunes. Songwriters' use of songwriting copyright gives them further control over how their works are used, including the ability to license their songs for use in movies, TV shows, advertising, and other types of media. The protection of songwriters' creative works and guaranteeing that they are fairly compensated for the usage of their music depend on this copyright protection.
Streaming services, radio airplay, TV advertising, live performances, and other methods can all be used to generate royalties. Depending on the terms of their individual contracts, the songwriter, composer, publisher, or performer may get royalties when a song is broadcast on the radio or streamed on a digital platform. The number of plays, song duration, and popularity are just a few of the variables that might affect how much royalties are paid. Usually, performance rights organizations are in charge of collecting royalties and distributing them to the relevant musicians.
Anyone working in the music business, whether as a songwriter, composer, performer, or publisher, must be aware of the various types of royalties: mechanical royalties, performance royalties, synchronization royalties, and print royalties. These days, there are even more royalty models emerging, largely thanks to the internet. Understanding how each type of royalty works is crucial for musicians in terms of optimizing income potential.
Mechanical music royalties are paid when a musical piece is duplicated, such as through physical copies or digital downloads. Usually, the author, composer, or publisher of the musical piece receives these royalties. Mechanical royalties are calculated differently depending on the nation and the specific agreements between the parties, but they are normally paid at a defined rate per unit of the duplicated work.
Music publishers, like Sony Music Publishing and Warner/Chappell, often collect mechanical royalties. The administration and licensing of musical works to different organizations, including record labels, streaming services, and digital platforms, is the responsibility of music publishers. Then, on behalf of the musicians whose works are being duplicated, they collect mechanical royalties.
You can learn more about publishing specifically, in our Guide To Music Publishing.
For the public performance of their musical compositions, songwriters, composers, and music copyright holders get compensation known as performance royalties. Live concerts, radio broadcasts, television shows, and other digital streaming services all fall under this category. The popularity of the music, the quantity of times it has been played, and the type of media used to play it can all affect the amount of performance royalties paid.
Performance rights organizations, like ASCAP or BMI, are responsible for collecting and distributing performance royalties in the majority of other nations. These organizations keep track of how musical compositions are used and receive royalties from the various users.
Sync royalties are payments provided to songwriters, composers, and music copyright holders for the use of their musical works in synchronization with visual media, such as movies, television shows, and commercials. Sync royalties are calculated differently depending on the exact agreements made between the parties, but they often entail a negotiated amount determined by the duration of the use, the song's popularity, and the media in which it is utilized. While sync royalties might not be as reliable as other kinds of royalties, they can nevertheless be a substantial source of income for musicians and are crucial to the music business.
Sync royalties are normally collected by music publishers, and royalties are distributed according to the terms of the agreement between the parties involved.
For the sale of sheet music or music scores that contain their musical compositions, songwriters, composers, and music copyright holders get payments known as print royalties. In the era of digital music, the sale of digital sheet music or other musical compositions, which can be done through a variety of digital channels, may also be included in print royalties.
Print royalties are frequently collected by music publishers on behalf of the music creators and are generally expressed as a percentage of the sale price of the printed music.
Newly emerging music royalty models, such as fan-powered royalties, are gaining attention in the music industry as a way to promote fairer and more equitable compensation for music creators. These models pay artists directly from the royalties received from streaming services based on the specific listening preferences of their fans. Several big players have already adopted these systems, such as Warner Music and Soundcloud. They aren’t perfect yet, but more new royalty models that attempt to offer fairer pay for music creators are likely to develop as the music industry continues to change in the digital age.
Through a combination of licensing agreements, usage monitoring, and payment processing, digital music services amass royalties. These are the fundamental steps you need to know:
It may seem like a straightforward process, but the music industry has a number of difficulties as a result of digital music royalties. These include complicated ownership and distribution, a lack of transparency, varying royalty rates, worldwide royalties, piracy, and a small amount of revenue sharing. Conflicts over royalties, postponed payments to rights holders, and decreased incomes for artists and other rights holders can all be consequences of these difficulties.
Spotify negotiates license arrangements with record labels, publishers, and collecting societies to obtain revenues for digital music streaming. Spotify tracks a song's consumption when it is streamed by using audio fingerprinting and metadata technology. The amount of royalties payable to the owners of the rights is then determined using the usage statistics. The royalty rate, which is based on a percentage of Spotify's earnings, might change depending on the listener's place of origin and the sort of subscription plan they have, among other things. Spotify collaborates with independent businesses who are experts in royalty collection and distribution to streamline the procedure.
Once a song is streamed or downloaded through Amazon Music, the platform keeps track of its usage and determines the amount of royalties due to the music's rights holders based on details including the song's duration and the number of streams or downloads. In addition, Amazon Music provides a service known as Amazon Music Unlimited, which charges a monthly subscription fee in exchange for access to a bigger music library. The royalty payments for songs played or downloaded via Amazon Music Unlimited are determined by a mix of membership revenue and the quantity of streams or downloads.
Apple Music tracks a song's usage after it has been streamed or downloaded using a combination of audio fingerprinting and metadata technologies. Based on usage data, Apple Music determines the amount of royalties owed to the rights holders, and normally pays a percentage of the money made by the service.
Through its Music Fund program, TikTok provides music creators and rights holders with a means of making money from the usage of their songs on the platform. With this arrangement, TikTok pays music creators and rights holders royalties based on how often their music is played. Although the cost per stream or use is not made public, it is said to be relatively affordable in comparison to other streaming services. Through a content moderation mechanism, TikTok also gives music rights holders the opportunity to claim and delete unauthorized usage of their music from the platform.
Instagram does not provide a standalone music streaming service, but it integrates with providers like Spotify and Apple Music to let users add music to their posts, stories, and reels. Instagram applies licensing and royalty fees for the usage of the music automatically when a user uploads a track to their Instagram content. Through connections that Instagram has with the pertinent music streaming providers, the fees are remitted directly to the rights holders. Instagram users can track their own use of music through the "Insights" function, which offers information on reach, impressions, and engagement for their music content, even if Instagram does not give extensive information about royalty rates or the distribution of revenues to rights holders.
As any gamer would know, Twitch is a platform for live streaming that enables users to share their gaming, musical performances, and other material with a large audience. In terms of digital music royalties, Twitch actually just launched a new program called Soundtrack by Twitch, which gives streamers access to a library of songs that are free to use during their broadcasts without worrying about violating any copyright laws. The system is run by a rights clearance service, and revenue sharing agreements are used to distribute royalties to the rights holders.
Music royalty collection and distribution organizations are entities in charge of collecting and distributing royalties on behalf of music rights holders such as composers, publishers, and performers. Assuring that rights holders are adequately compensated for their work when it is played or performed in public, these organizations play a crucial role in the music industry.
Around the world, there are a number of significant organizations that collect and distribute music royalties, including ASCAP, BMI, and SESAC in the United States; PRS for Music in the United Kingdom; SACEM in France; and others. These businesses often have a non-profit mission and work to maximize revenue for rights holders while making sure they receive timely and accurate payments.
Generally, music royalties are paid by way of direct deposit, and the frequency of payment depends entirely on the agreement you have with your distributor. The method in which the payment amount is calculated and dispersed can vary, including:
Depending on the exact agreements between the rights holders and the related collection and distribution organizations, music royalty payment schedules might vary significantly. However, in general, royalties are paid out on a quarterly or semi-annual basis. Depending on the style of music, the nation of origin, and the distribution methods utilized, the precise timing of these payments may change.
Any musician or owner of music rights who wants to obtain royalties for the usage of their music should register with music royalty collection societies. Musicians who register can make sure that their music is accurately monitored and that they are paid when it is played or performed in public. Typically, in order to register, musicians must supply basic information about themselves, their music, and their style of composition, including the titles of their songs, the names of the composers and publishers, and the genre of music they produce. With this data, each song is given a special identifying code that the collection societies can use to precisely track and distribute the royalties.
For musicians and rights holders to guarantee they are paid fairly for their work, it is crucial that they comprehend and properly negotiate music royalty contracts. This entails carefully going over the contract's terms and conditions, such as the amount of royalties, how they will be distributed, and the range of the rights given. Additionally, musicians should be informed of any fees or deductions from their royalties that may be made, such as marketing or administrative fees.
Musicians can take steps to make sure that their music is used legally by monitoring its use and registering their compositions with music rights groups. Musicians can protect their rights to fair compensation for any use of their works and the opportunity to pursue legal action against unlawful use by registering their music. Musicians may keep track of how their music is being used by using technologies like music recognition software, which can detect when it is broadcast on the radio or played in public places. If unauthorized usage is discovered, musicians can take the necessary steps to protect their intellectual property and recover any royalties owing to them by working with their legal counsel and music rights organizations.
The most common legal issue related to music royalties is copyright infringement. When someone uses, reproduces, distributes, or performs music that is protected by a copyright without the owner's consent, that is considered copyright infringement. This can involve exploiting copyrighted music samples in unlicensed new compositions, sharing unlicensed copyrighted music online, or performing unlicensed copyrighted music in public without paying the required performance fees. Infringing content may be removed from internet sites as well as subject to legal action, fines, and other consequences. Musicians and owners of music rights need to be on the lookout for copyright violations and take appropriate measures to protect their intellectual property.
Another common legal issue surrounding music royalties is ownership dispute. This often happens when different parties assert ownership or entitlement to a share of the royalties produced by a specific song or piece of music. Particularly in situations where ownership or usage rights were not expressly stated in contracts or agreements, these conflicts can be complicated and controversial. Changes in ownership, such as the sale or transfer of the rights to a song or a music library, can also result in disputes over music royalties. Parties may need to resort to litigation or mediation to settle disagreements over music royalties in order to establish ownership and distribution rights.
Musicians can collect music royalties by registering their works with music rights organizations and royalty collection agencies. Once their works are registered, the organizations will monitor the use of the music and distribute royalties to the appropriate rights holders.
Much like musicians, you must first make sure the song is registered with a music rights organization or royalty collection agency in order to begin collecting music royalties. These organizations will trace the consumption of your music and will collect royalties on your behalf. Additionally, you must guarantee that your music is utilized with the appropriate permissions and licenses, monitor usage to ensure fair pay, and, if required, take legal action to enforce your rights. By taking these actions, you may safeguard your intellectual property as a rights holder and make sure that you are fairly reimbursed for the usage of your music.
A songwriter and a publisher earn different sorts of income for the use of their music. A songwriter is compensated with royalties for the creation of the music, as well as for its mechanical and live performance. Usually, the music rights organizations or royalty collection companies pay the songwriter these payments.
A publisher earns royalties for the exploitation of the song, such as licensing the song for usage in TV, cinema, or ads. Publishers also receive mechanical royalties when a song is replicated on tangible media like CDs and vinyl. The publisher normally receives a portion of these royalties as compensation for their part in marketing and promoting the song, with the remaining funds going to the songwriter.
Depending on the sort of royalty and the legislation in the country where the song was made, the length of music royalties varies. In general, royalties from music might extend for decades or even longer.
You can indeed receive royalties for a cover song. A mechanical license is required to publish your version of the music legally since, when you cover a song, you are producing a derivative work based on the original composition. Mechanical licenses, which you can purchase for a predetermined sum or royalty rate from a music rights organization or the publisher of the original song, allow you to duplicate and distribute your version of the song. You can also use a distribution service that handles all of this for you.
In order to do this, you have to follow a few steps. First, of course, register your song with a performing rights organization. Then, to make it easier for music supervisors and licensing agents to find your music, make a music library with information about each piece. Make use of online music licensing resources like AudioJungle and Pond5 and bargain the license agreement's conditions. You can improve your chances of getting your music licensed and making more money by aggressively promoting your music.
Your heirs will normally receive your music royalties in accordance with your will or local inheritance rules. To make sure that your music royalties are distributed how you want them to be, it is crucial to have a will in place. To manage your music royalties and carry on collecting royalties from your music after your passing, your heirs may need to consult with a lawyer or member of the music business.
Keep thorough records of the songs you release, the gigs you have planned, and the royalties you have been paid. To make sure you are receiving the correct payment for the use of your music, regularly check your performance rights organization and other sources' royalty statements.
Make sure to copyright your music with the U.S. Copyright Office, register it with a performing rights organization, and exercise caution when signing licensing agreements. Maintain thorough records of your music releases, concert dates, and royalties paid, and keep an eye on how your music is used to make sure you are getting paid fairly for your work as a songwriter or publisher.

As you can tell, music royalties play an important role in the music industry by ensuring that rights holders, such as musicians and composers, are compensated for the use of their works.
Musicians now have new opportunities to reach audiences and make money through streaming and other digital platforms, as well as new issues related to the collection and distribution of royalties, thanks to the complicated and constantly changing digital music ecosystem. By properly registering their compositions and collaborating with respected music rights organizations and revenue collecting companies, musicians can increase their earnings.
All that's left to do now is make some tracks that will earn you some royalties. When you do, make sure you promote music using social media to reach an ever wider audience for your shows and streaming channels.
